Hands-on work: Laboratory Practices
September 2011 - July 2017
Over the years I spent at my university, studying and working hard to become the best Mechanical Engineer, I had the opportunity to participate in several laboratory practice of many academic courses, such as: Physics, Fluid Mechanics, Manufacturing Processes, Energy Conversion, Machine Vibrations, Machine Dynamics, Heat Transfer, Machine Design, and Material Science.
Universidad Simón Bolívar.
Caracas, Venezuela.

1. Molding and casting.
2. Tensile test.
3. Hardness test.
4. Non-destructive testing: visual inspection, penetrating liquids, magnetic particles, ultrasound.
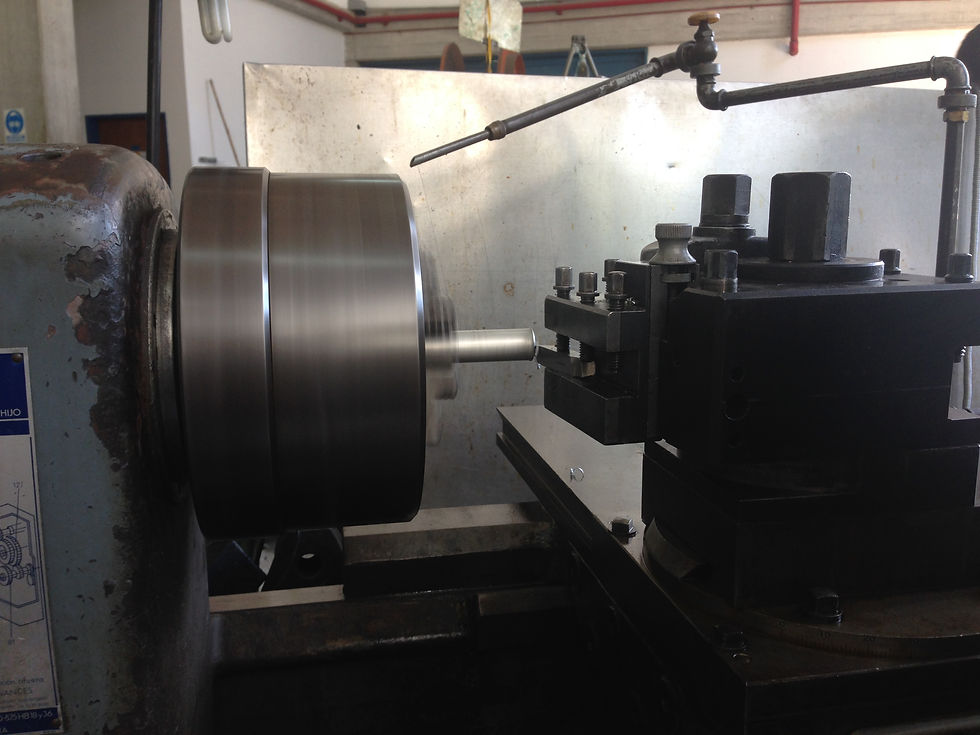
5. Machining: manufacturing processes with a set of operations of shaping parts by removing material, either by chip removal or by abrasion. Among the machines we used in the laboratory are Lathe, Drill, Brush, Milling Machine and Reformer.
6. Machining by numerical control (CNC).
7. Equipment and processes of welding, microstructure and hardness.
Manufacturing Processes.
1. Simulation of a vehicle motor-radiator system
2. Cross flow – heat exchanger
3. Refrigeration system
4. Temperature profiles
5. Non-stationary conduction
6. Calibration of thermocouples
7. Thermail dilation
8. Double tube-heat exchanger
9. Double tube-heat exchanger/tube and shell
10. Viscous laminar heat exchanger
11. Cross flow-heat exchanger: free and forced convection
12. Thermal radiation
Heat Transfer.


















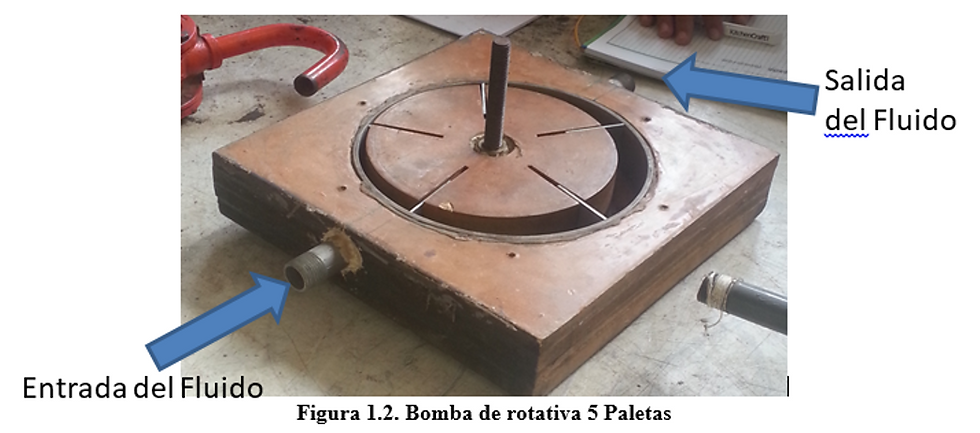
Enery Conversion.
1. Reciprocating and Diaphragm Pumps: The practice was focused on the study of displacement pumps, specifically one rotating and two reciprocating type. The rotary pump that was studied was one with blades, and the reciprocating ones were one of pistons (the one which was disarmed) and one of diaphragm.
At a glance, it could be seen that the reciprocating piston pump is a triple action pump, since it has three pistons which each can complete a single action, either loading or unloading, but operating together, the triple action behavior occurs.
2. Progressive Cavity Pump: practice of experimental data collection and performance analysis.
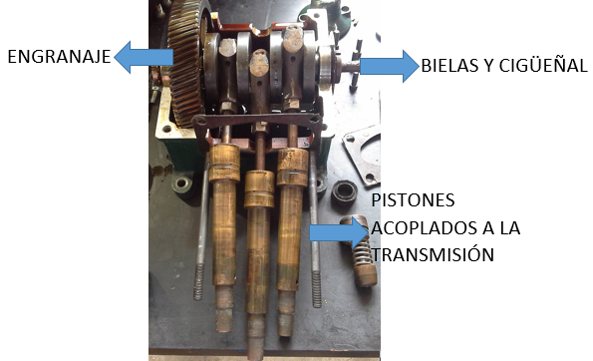
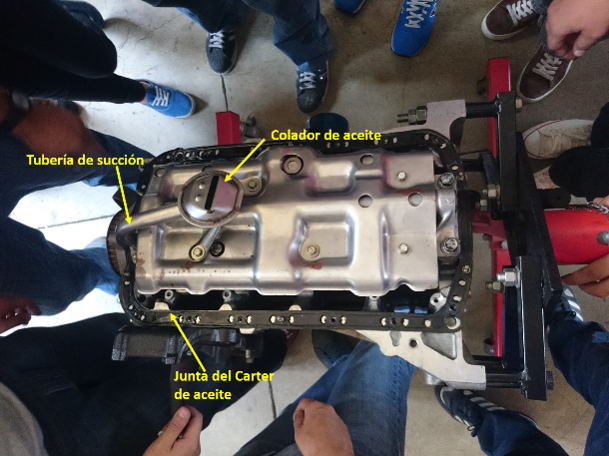
3. Internal Combustion Engines: In the laboratory practice, a Honda internal combustion engine was disassembled to identify its different parts and to analyze its operation.
Physics.
-Electric measurements with the oscilloscope
-Electronic circuits
-Electric measurements with the multimeter
-Electrical fields
-Electric resonance
-Damped oscillations
Among others.


















Machine Vibrations:
1. Free vibrations: Test station of dampers.
2. Forced vibrations with one degree of freedom.
3. Forced vibrations with two degrees of freedom.
Machine Dynamics:
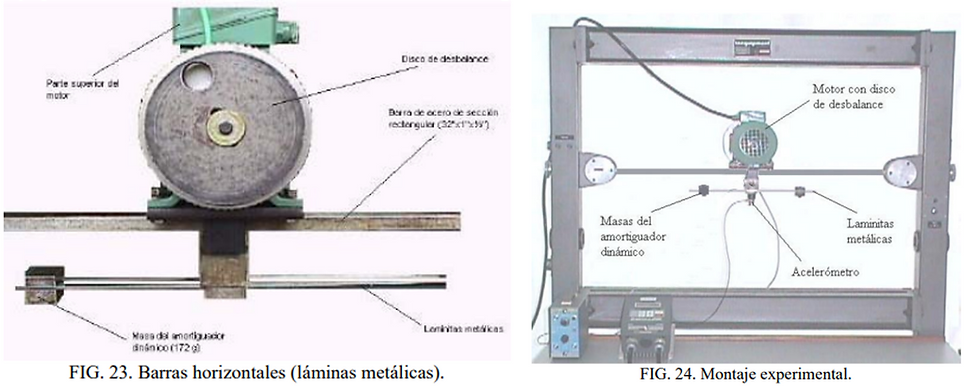
1.Balancing conditions of a rigid rotor.
2.Dynamic balance of a flat rotor.
3.Dynamic balance of a rotor with two planes.
Machine Dynamics and Vibrations.
Fluid Mechanics.
1.Physical properties of fluids determination, and manometers calibration
2.Hydrostatic forces of submerged objects and Demonstration of Bernoull's Theorem
3.Impulse and amount of movement
4.Turbulent flow in smooth pipes
5.Flow measurement instruments calibration
6.Oscillations tower





























-The Torque Wrench is a precision tool, which is used to apply a certain tension in screws, nuts, bolts, among others. In the first lab-practice I identified the material of a part by calculating its resistance to creep using the torque wrench.
-In the second lab-practice I identified the material and type of some screws, having studied their failure to cut after a force was applied to them. The threaded joints fail by crushing (they begin to deform) until they break due to the cut, here the calculation was made with the necessary force for the failure to cut.
Machine Design.
Materials Science.
1. Metallography: Cutting and surface preparation. Polishing and chemical attack. Photomicrographs.
2. Thermal Treatments and Traction Test.
3. Jominy Test and Hardness Measurement.
Personally, I enjoyed this university course. It was very entertaining, and I would be very grateful for any opportunity to put this knowledge in practice. I learned about:
-Control systems (Open/Closed Loop, Linear/Non-linear, Continuous/Discrete).
-Modeling of Physical Systems.
-Linearization of non-linear models.
-Reduction of block diagrams and signal flow diagrams.
-Transient Response of a System.
-Analysis of Closed Loop Systems.
-Design of Industrial Controllers.
-Instrumentation.
Control and Instrumentation.



